Hip Bursitis Specialist
Do you have pain in the hip that causes you to limp or lose sleep? You may have a hip condition called trochanteric bursitis. Trochanteric bursitis specialist, Doctor Prem Ramkumar, offers surgical and non-surgical treatment options for patients who have trochanteric bursitis, He is located in Long Beach and serves patients in Los Angeles, Orange County, and surrounding Southern California areas. Contact Dr. Ramkumar’s team today!

What is trochanteric bursitis?
The greater trochanter is the bony prominence of the femur (thigh bone) you can feel when you place your hand on the outside of your hip. When moving your leg, the greater trochanter slides smoothly and painlessly past where the abductor tendons and iliotibial (IT) band meet. This motion is made possible thanks to the trochanteric bursa, which has fluid-filled sacs that lubricate the area to allow otherwise pain-free motion. If the bursa becomes inflamed, the joint no longer moves smoothly and can become painful – a condition known as trochanteric bursitis. Trochanteric bursitis is common in older patients and may represent early irritation, injury, or tearing of the abductor tendons. Dr. Prem Ramkumar, trochanteric bursitis specialist, is located in Long Beach and serves patients in Los Angeles, Orange County, and surrounding Southern California areas.
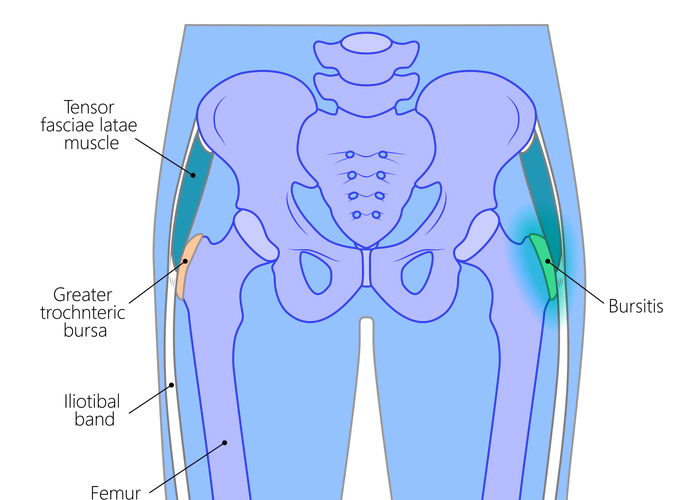
What causes trochanteric bursitis?
The bursa’s job is to provide a friction-free cushion between the prominent greater trochanter bone and the tendons that allow the leg to bend, move, and rotate without a limp. When the bursa is inflamed, it causes pain (particularly at night) and sometimes a limp. Some people are more susceptible to trochanteric bursitis than others. Causes can include:
- Underlying bone structure – patients who have unique anatomy (coxa vara) are more prone to this
- Hip injury – Traumatic bursitis caused by a fall or a hit to the hip can cause the bursa to fill with blood and the lining to become inflamed.
- Repetitive hip pressure– Caused by frequent mini-traumas, or overuse and often seen in individuals who run, walk, bike, or stand for long periods.
- Age and sex – Most often, individuals age 40 – 60+ are more likely to develop trochanteric bursitis, and women are more likely to report this specific type of pain in the side of the hip than men (due to differences in the pelvis shape)
What are the symptoms of trochanteric bursitis?
The most common symptoms of trochanteric bursitis are pain in the hip directly over the bump that forms the greater trochanter and pain that radiates down the hip to the outside of the thigh. Other symptoms include:
- Limping
- Swelling in the affected leg
- Dull ache outside the joint
- Pain that keeps you up at night
- Stiffness and trouble walking after sitting too long
How is trochanteric bursitis diagnosed?
During your office visit, Dr. Ramkumar will perform a history and physical exam looking for tenderness and tightness along the abductors and iliotibial band. An X-ray will help determine if any other conditions may be causing the pain, from abductor tendon tears to femoracetabular impingement to osteoarthritis. In some cases, an MRI may be necessary to ensure the trochanteric bursitis is not actually an abductor tendon tear.
How is trochanteric bursitis treated?
Non-Surgical Treatment:
Most patients suffering from trochanteric bursitis will never need surgery. Patients are encouraged to modify their activity levels, especially if they play sports, and start a physical therapy program to stretch and strengthen the joint. Anti-inflammatory medications, such as NSAIDs, can help reduce inflammation. Dr. Ramkumar will almost never recommend a cortisone injection as this weakens the underlying tendons and may rupture them – potentially leading to disability and surgery. With non-surgical treatment, a patient should typically improve from trochanteric bursitis in about 8-12 weeks.
Surgical Treatment:
If non-surgical treatments do not provide relief and the trochanteric bursitis has progressed to the point of becoming an complete abductor tendon tear with unremitting pain and disability, surgery may be necessary to address this. Dr. Ramkumar may performs surgery to clean up and remove the excess bursa, as well as repair the abductor tendon.

