Patellar Injury Specialist – Knee Tendonitis, Tendinosis, Tendon Tear or Fracture
- Knee Tendonitis: Also called ‘Jumper Knee’ – this happens when the patellar tendon becomes inflamed.
- Patellar Tendinosis: This occurs when knee tendonitis becomes chronic or reoccurs
- Patella Tendon Tear: The tendon tears away partially or entirely from the patella attachment site.
- Knee Cap0 Tendon Tear: The tendon tears away partially or entirely from the kneecap’s attachment site.
- Patella Fracture: The kneecap bone breaks
Do you have knee pain that’s getting worse? Maybe your kneecap moves around? You may have a patellar tendon injury. Knee Tendonitis, also called “Jumper’s Knee”, happens when the patellar tendon becomes inflamed. Patellar Tendinosis occurs when knee tendonitis becomes chronic or reoccurs. A Patella Tendon Tear occurs when the tendon tears away partially or entirely from the patella attachment site. In a Patella Fracture, the kneecap bone breaks. Knee specialist Dr. Prem N. Ramkumar provides non-surgical and surgical treatments for patients with patellar tendon injuries. His office is in Long Beach and serves Los Angeles, Orange County, and surrounding Southern California areas. Contact Dr. Ramkumar’s team for an appointment today!

What is a patellar tendon injury of the knee?
Tendons are fibrous connective tissues throughout the body connecting muscles to bones. Unlike ligaments that keep a joint stable, tendons help muscles move. The patellar tendon attaches the bottom of the patella (kneecap) to the top of the tibia (shin bone). Both the patellar tendon and the quadriceps tendon must move in unison to properly straighten the leg. If any muscles, ligaments, or tendons are inflamed or torn, it can cause patellar tendon pain or, in extreme cases, inability to straighten the leg. Dr. Prem N. Ramkumar, patellar tendon injury specialist, is located in Long Beach and serves Los Angeles, Orange County, and surrounding Southern California areas.
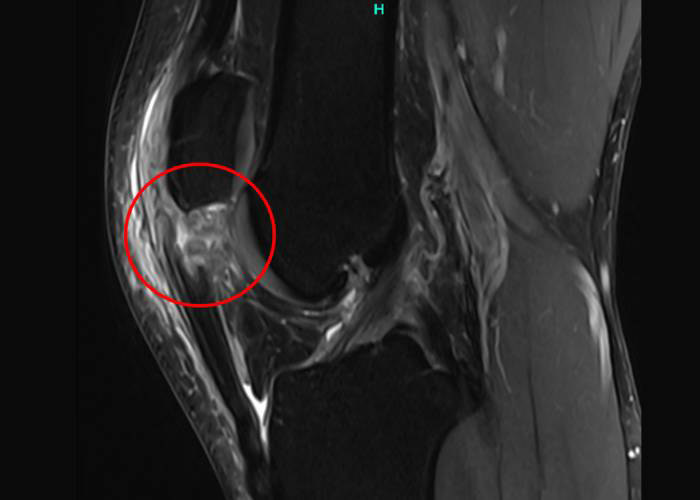
What are the types of patellar tendon injuries of the knee?
A knee dislocation, a tackle on the football field, a degenerative condition, or a genetic predisposition can all cause a patellar tendon injury. Athletes who participate in sports requiring repetitive running or jumping are most likely to suffer attritional patellar tendon injury. A patella tendon tear can also happen from a fall or an automobile accident. A small patellar tendon tear cause difficulty walking or climbing stairs, while a large tear will make it impossible. The most common causes of a patellar tendon injury are:
- Knee Tendonitis: Also called “Jumper’s Knee” – this happens when the patellar tendon becomes inflamed.
- Patellar Tendinosis: This occurs when knee tendonitis becomes chronic or reoccurs
- Patella Tendon Tear: The tendon tears away partially or entirely from the patella attachment site.
- Patella Fracture: The kneecap bone breaks
What are the symptoms of a patellar tendon injury of the knee?
Pain is typically the first sign of a patellar tendon injury. Weakness with inability to straighten your knee, including activities like walking and climbing stairs, can also be difficult and a sign of a complete tear. Other symptoms include:
- Knee tenderness
- Bruising and cramping in the knee
- Indentation at the bottom of the patella (tendon rupture)
- Patella (kneecap) that moves around and is no longer attached to the tibia
How is a patellar tendon injury of the knee diagnosed?
Dr. Ramkumar will perform a thorough knee examination to determine the exact cause of your symptoms and pain. He will also obtain a complete medical history and ask about previous knee injuries. In addition to a physical exam, Dr. Ramkumar may also order imaging tests such as an MRI scan so he can see inside the knee joint and confirm the diagnosis.
How is a patellar tendon injury treated?
If you suffer a patellar tendon injury, early intervention prevents the tendon from retracting into the knee and accumulating scar tissue. Non-surgical treatments are usually the first option for patella tendon pain, small tears, or tendonitis. They include immobilization with a knee brace and physical therapy to restore function and mobility.
If non-surgical treatments do not ease your pain, or you have a complete patella tendon rupture, Dr. Ramkumar can repair, reattach, or reconstruct the tendon with a surgical procedure. In certain cases, arthroscopy or a minimally invasive approach may be performed to remove the inflamed tissue for partial tears. If you follow post-operative protocol, recovery from surgery to repair the patellar tendon can take an average of 4-6 months.

